polar definition chemistry
Polar Bond Definition. A molecule may be polar or non-polar.

Polar Bond Easy Science Covalent Bonding Chemistry Bond
Most carbon compounds are nonpolar.
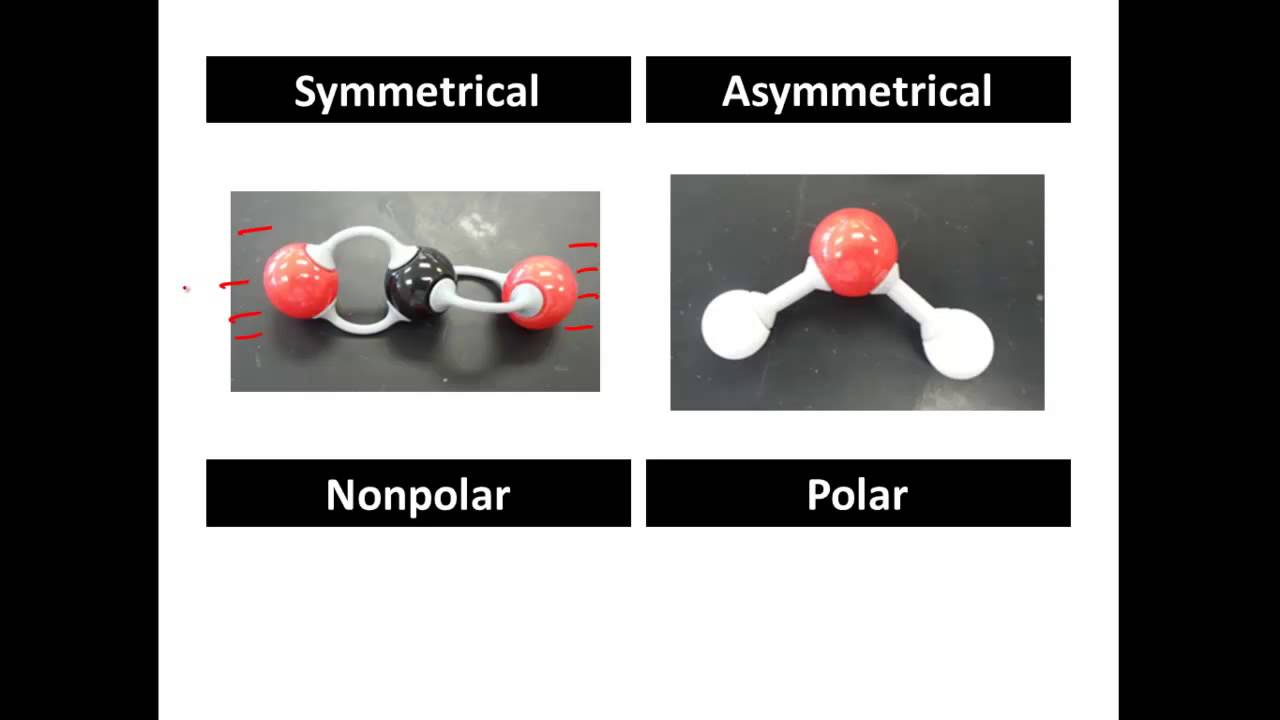
. A diatomic molecule that consists of a polar covalent bond such as HF is a polar molecule. Definition of Polarity A state or a condition of a molecule having positive and also negative charges particularly in case of magnetic or electrical poles. It has a region of partial charge. Time Traveler for polar.
How to use polar in a sentence. Examples of homonuclear nonpolar molecules are oxygen O 2 nitrogen N 2 and ozone O 3. Polarity Chemistry - Polar and Non-Polar Molecules. A polar molecule is a molecule containing polar bonds where the sum of all the bonds dipole moments is not zero.
Directly opposite in character or tendency Not to be confused with. Molecules containing polar bonds have no. While there is no net charge to a water molecule the polarity of water creates a slightly positive charge on hydrogen and a slightly negative. Polar bonds form when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms participating in a bond.
Polar synonyms polar pronunciation polar translation English dictionary definition of polar. Waters Polarity One of waters important properties is that it is composed of polar molecules. A polar bond is a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed. The meaning of POLAR is of or relating to a geographic pole or the region around it.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. In chemistry polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multi-pole moment. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Polar molecules also form when the spatial arrangement of chemical bonds leads to a more positive charge on one side of the.
It has one slightly positive end and one slightly negative end. All molecules have a permanent number of electrons which are arranged at certain energy levels called a shell. Well moreover the polar solvents possess molecules with polar bonds and nonpolar solvents possess molecules with similar electronegativity values. The first known use of polar was in 1556.
Polarity in chemical bonding the distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond. How to use nonpolar in a sentence. In chemistry the definition of a polar molecule is a molecule that has a charge on one side of the molecule that is not canceled out. The charge of the electric dipoles is less than a full unit charge so they are considered partial.
Nonpolar Molecule Examples. The electrons are generally asymmetrical with an uneven distribution. Specifically while bonds between identical atoms as in H 2 are electrically uniform in the sense that both hydrogen atoms are electrically neutral bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent. The meaning of NONPOLAR is not polar.
Post the Definition of polar to Facebook Share the Definition of polar on Twitter. The two electrically charged regions on either end of the molecule are called poles similar to a magnet having a north and a south pole. When grease or oil non-polar hydrocarbons are mixed with a soap- water solution the soap molecules work as a bridge between polar water molecules and non. This causes the molecule to have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative.
Pertaining to the North or South Pole. In chemistry polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Water is a polar molecule and also acts as a polar solvent. Water alone is not able to penetrate grease or oil because they are of opposite polarity.
This video explains polar and non-polar characteristics in detail. In general pyramid-shaped and V-shaped molecules are said to be polar. A notable exception is carbon monoxide CO. When a chemical species is said to be polar this means that the positive and negative electrical charges are unevenly distributed.
This is due to the shape of the molecule. A polar molecule is a molecule in which one end of the molecule is slightly positive while the other end is slightly negative. A non-polar molecule has a structure of its atoms lined up in a way that the orbital electrons in the outer region cancel out the electronegativity. The hydrogen and oxygen within water molecules H2O form polar covalent bonds.
The non-polar hydrocarbon tails are repelled by the water which makes them appear to stand up. A substance that contains polar covalent bonds may not be overall polar. The positive charge comes from the atomic nucleus while the electrons supply the negative charge. Polar and non-polar molecules.
Whereas the Linear molecules are said to be non-polar in nature. See more words from the same year. The prime difference between polar and nonpolar solvents is the polar solvent gets dissolved in a polar compound whereas the non-polar solvent gets dissolved in non-polar compounds. Consisting of molecules not having a dipole.
The electrons present. Other nonpolar molecules include carbon dioxide CO 2 and the organic molecules methane CH 4 toluene and gasoline.

Difference Between Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Definition Formation Properties Examples Covalent Bonding Chemical Bond Study Chemistry

Polar And Non Polar Covalent Molecules Polar Vs Nonpolar Youtube Playlist Science Chemistry Chemistry Molecules

Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Covalent Bonding Chemistry Lessons Molecules

Why Is Water A Polar Molecule Water Molecule Polarity Of Water Molecules

Definition And Examples Of A Polar Bond In Chemistry Covalent Bonding Chemistry Chemical Bond
Komentar
Posting Komentar